Spotlight
-
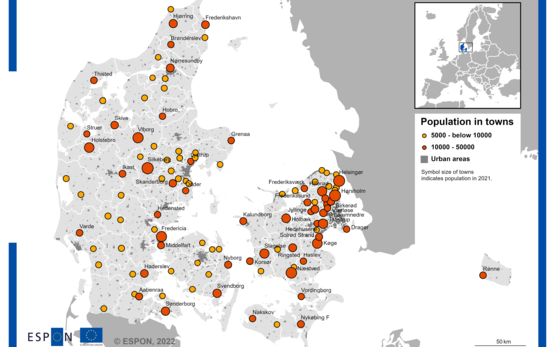
Denmark, small and medium sized cities
Case Studies | August 25, 2022Looking for new activities and attractions to maintain vibrant town centres and develop appealing urban areas

Looking for new activities and attractions to maintain vibrant town centres and develop appealing urban areas

This report contributes to the Maritime Spatial Planning with two objectives: to undertake an analysis and characterization of the coastal and maritime planning and land-sea interactions from a mul

Article 174 of the TFEU states that: '’the Union shall aim at reducing disparities between the levels of development of the various regions and the backwardness of the least favoured regions.

This project, emanating from the targeted analysis project Maritime Spatial Planning and Land Sea Interactions (MSP-LSI) explores the potential spatial tensions between the deployment of renewable sources of blue energy (energy derived from our seas and oceans), with a particular focus on offshore wind energy, and other (potential) utilisations of the European seas.

This study analyses the implementation of an Integrated Territorial Investment (ITI) targeting small islands of the North Aegean Region in the 2014-2020 programming period, considering observed pat
This policy brief aims to help European, national, regional and urban authorities to better understand the level of digitalisation of public services, to learn from others through benchmarking and to design actions for the future.
The purpose of this Policy Brief is to identify shrinking rural regions and where they are located in Europe; explore key development challenges and opportunities; examine some policy responses using case study examples from shrinking rural regions; and present some emerging policy recommendations at European, national and sub-national levels.
This paper aims at informing policy-makers at the EU level about the benefits and added value of the interregional programmes in times of resource scarcity.
March 2017 - ESPON presents territorial observations on key development patterns of territories with geographic specificities (coastal areas, islands, mountains and sparsely populated regions) and key messages for policy-makers for designing and implementing development strategies specifically tailored to the needs of these places.

In times of decreasing resources and growing responsibilities, a transition to a circular economy is both a necessity and an opportunity for cities and regions, with the potential to offer long-lasting economic, environmental and social benefits. Many local and regional authorities are already making efforts towards a more circular economy.

Polycentricity is a concept that encourages regions and cities, working with neighbouring territories, to explore common strengths and reveal potential complementarities, which brings added value that cannot be achieved by the individual regions and cities in isolation.

More than ever, cities today need to reinforce smart, sustainable and inclusive growth, while managing e.g. demographic change, housing, urban mobility, energy transition, all in a context of scarce public but also private resources.

Over the last years, the movement in favour of an integrated European urban policy has gained momentum. Improving urban quality of life, addressing social challenges in cities, facilitating mobility and communications and ensuring that all cities fully contribute to national economic growth and job creation are important and interlinked objectives.

Better Regulation, with the aim to lead to EU policies achieving their objectives in the most effective and efficient way, is one of the central themes of the Dutch EU-Presidency. Upon request the ESPON EGTC analysed possible long-term effects in case the design and implementation of the regulatory framework would not be aligned with Better Regulation.

Territorial scenarios focusing on the development of metropolitan regions, of cities or of regions will towards 2050 deliver the same level of economic growth for Europe. However, attention to the development of cities seems to have a slight advantage towards 2030.

Europe has witnessed an inflow of a large number of people over the last years. As a consequence of the geopolitical instability in the Middle East and Africa, migration and refugee flows towards Europe have increased with significant territorial impacts on European countries, regions and cities.